Support vulnerability management for Security Officer
Information Gathering
Centralized management of diverse system components
- It covers paid middleware, application-dependent libraries, WordPress plug-ins, as well as Linux, Windows, containers, network equipment firmware, and more. (List of supported environments)
Automatically collects vulnerability information released daily from a wealth of information sources
- FutureVuls automatically collects new vulnerability detection and updates from multiple data sources, including NVD, JVN, Red Hat, Amazon Linux, and GItHub, on behalf of our customers.
- In addition to alerts issued by JPCERT/CC and US-CERT, the "Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog" ("CISA-KEV") published by the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Administration (CISA) is also automatically collected. ("CISA-KEV") published by the U.S. Cyber Security and Infrastructure Security Administration (CISA) is also automatically collected.
- Attack code (POC and Exploit) information collected from Metasploit Framework, ExploitDB, NVD, GitHub repositories, etc. with confidence levels.
- Many sources of information
Also detects vulnerabilities where no CVE-ID is assigned
- Many application library vulnerabilities are not assigned a CVE-ID, but we can also detect vulnerabilities not covered by the CVE-ID that are covered by the vulnerability information dedicated to each language.
Also detects vulnerabilities in Japanese software
- Vulnerabilities in "Japanese software that is not included in NVD but has vulnerability information registered in JVN" such as products for Japan can also be detected.
Impact assessment, prioritization and response decisions
Understand if vulnerable software is running
- Automatically perform impact studies, such as identifying software affected by disclosed vulnerabilities.
- The display shows whether the process associated with the software for which a vulnerability has been detected is running on the server or listening with a network port open, allowing prioritization taking into account information about the process.
Reliable, proven scanner for accurate impact studies
- NVDs and JVNs contain the version of the software origin (upstream) and are different from the version numbers of package management tools such as `rpm` and `deb`. FutureVuls detection logic is based on OSS, which has been improved more than 1000 times by more than 100 developers from all over the world, and can correctly evaluate a vast amount of data sources. FutureVuls detection logic is based on OSS, which has been improved more than 1000 times with the participation of more than 100 developers from around the world.
| Linux distribution | modified version |
|---|---|
| upstream | 2.4.52 |
| Red Hat Enterprise Server 6, 7 | No impact |
| Ubuntu 18.04 | 2.4.29-1ubuntu4.21 |
| Ubuntu 20.04 | 2.4.41-4ubuntu3.9 |
| Debian Strech | 2.4.25-3+deb9u12 |
| Debian Buster | 2.4.38-3+deb10u7 |
| Amazon Linux2 | httpd-2.4.52-1.amzn2.x86_64 |
Compare and supplement multiple vulnerability information for decision making
- It displays a summary description of the vulnerability, CVSS vectors, CWE, public agency alert information, publicly available attack code, distribution support pages, and other helpful URLs from multiple data sources, including NVD, JVN, Red Hat, Microsoft, and others.
- The impact on "confidentiality", "integrity," and "availability" of the vulnerabilities can be checked in the CVSS published by JVN and NVD.
- Displays the presence or absence of attack code (Exploit), along with the confidence level of the attack code information collected from Metasploit Framework, ExploitDB, GitHub repositories, and other sources.
Cross-control of vulnerabilities across all systemsCSIRT plan
- Multiple systems (groups) can be bundled and managed across groups. (Group set function)
- The group set function bundles multiple systems into one for cross-sectional management, enabling impact investigations and decisions to be made from the screen at once.
Instantly identify the impacted area of the vulnerability you want to investigateCSIRT plan
- The software cross search function allows you to search across software in use in your company. The search results include system, server, and version, so that, for example, a vulnerability that was in the news this morning and is too new to be registered in the vulnerability database yet can be cross-searched by software name on the screen, and the impact can be investigated based on the version number.
Flexibly define your organization's response policy and extract only high-risk vulnerabilities
- Judging by CVSS score alone, the number of targets is too large for the operation to turn around.
- High-risk vulnerabilities can be pre-defined according to the customer's security policy, such as "Red Hat CVSS score of 7 or higher," "network attackable," "attackable without authorization," and "publicly disclosed attack code," etc., allowing flexible filtering of high-risk vulnerabilities. High-risk vulnerabilities can be filtered out flexibly.
- Security personnel can save rules for high-risk vulnerabilities on a group basis. Operations can prioritize high-risk vulnerabilities automatically filtered by rules.
Decisions are completed on FutureVuls
- All information necessary to make a decision is listed on the screen, so there is no need to check the status of individual systems with the operations staff.
CVSS score plus a combination of user environment and risk conditions
- Judging solely by CVSS scores will result in a large number of targets to be addressed, making actual operation difficult.
- Judgments can be made based on a combination of risk factors other than the CVSS score. CVSS can also be recalculated according to the system environment and the presence or absence of published attack code.

Implementation and Management
Alerts operators immediately to high-risk vulnerabilities
- Using the Topic function, you can share information within your organization by posting the results of investigations into vulnerabilities and the degree of danger. In addition, by designating vulnerabilities that must be addressed as Danger, they can be prominently displayed in the vulnerability list and detailed view screen, which is useful for alerting the public.
- The automatic alert function CONTRAST ERRORS: Very low contrastCSIRT plan automatically alerts the organization of high-risk vulnerabilities according to predefined rules, and the automatic hiding function CONTRAST ERRORS: Very low contrastCSIRT plan automatically hides tasks for vulnerabilities judged to be low-risk: Very low contrastCSIRT plan, which automatically hides tasks for vulnerabilities deemed low-risk.
Tracking the status of responses to vulnerabilities that have been brought to your attention
- The response status of vulnerabilities alerted by Danger designation in the Topic function can be checked across the system. The response status can be tracked on the screen, such as whether the operator has updated the software or bypassed the vulnerability through configuration.
- The task comment function allows operators to check the status of vulnerability responses, give instructions for responses, and manage progress.
Report to Management
Reporting of newsworthy and critical vulnerabilities as a management risk to your company quickly.CSIRT plan
- The group set function enables cross management of multiple groups (systems), so you can see the company-wide impact at a glance.
- Software cross search function allows you to search and identify specific software in the group set. For example, in the case of Log4shell, software search by "log4j" will show the corresponding system, server and version. This is also useful in terms of asset management.
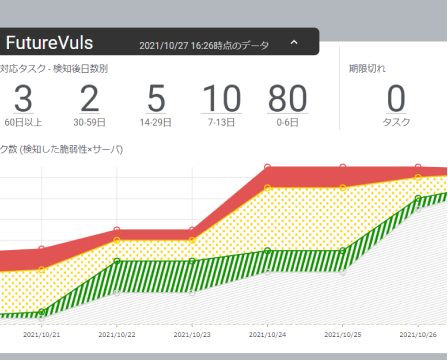
Visualize and report on group response progress, and understand vulnerability response details by systemCSIRT plan
- The dashboard function displays the number of vulnerabilities in each group, the number of days since the task was created, and the task response status. You can see at a glance which groups are responding smoothly and which groups are lagging behind, and view a list of vulnerability response status by system.
- You can also use it for system audit because the comment of the task contains the details of the response status.